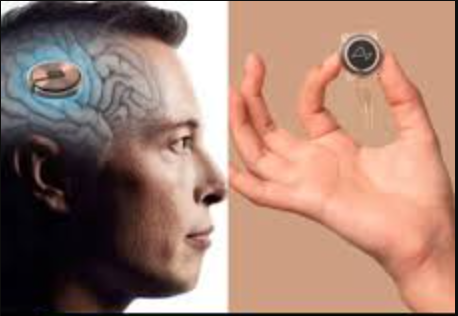
Elon Musk, a name synonymous with groundbreaking ventures such as Tesla, SpaceX, and The Boring Company, has turned his attention to one of the most ambitious projects of his career: Neuralink. This neurotechnology company, co-founded by Musk in 2016, is working to develop a revolutionary brain-computer interface (BCI) that could change the way humans interact with technology. But what sets Neuralink apart is Musk’s vision for affordability and accessibility. In a recent statement, Musk suggested that in the future, Neuralink’s BCI could be as affordable as an Apple Watch, opening the door for the technology to be used by millions of people around the world. This article explores the potential implications of such an ambitious goal and the technology behind it.
What is Neuralink?
Neuralink is a company that is focused on developing high-bandwidth, implantable brain-computer interfaces. The goal of these BCIs is to allow the human brain to communicate directly with external devices such as computers, smartphones, or even robotic limbs. The potential uses of this technology are vast, ranging from medical applications—such as treating neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and paralysis—to enhancing human cognitive abilities by allowing direct interaction with AI systems or augmented reality.
At its core, Neuralink’s technology consists of tiny, flexible threads embedded into the brain, which connect to a small, coin-sized chip. The threads are thinner than a human hair and are designed to be implanted into the brain with minimal damage to surrounding tissue. This chip, which acts as the interface between the brain and external devices, can read electrical signals in the brain and send those signals to a computer.
The key difference between Neuralink’s technology and other BCIs currently in development is its ability to transmit large volumes of data at high speed. This would theoretically allow for complex, real-time interactions between the brain and machines. While other BCIs exist for medical purposes, they often suffer from limited bandwidth, making them less capable of real-time applications.
The Dream of Affordability
In the world of cutting-edge technology, one of the most pressing questions is often: “How much will it cost?” Musk has always been a proponent of making futuristic technologies accessible to as many people as possible. This is evident in his work with Tesla, where he has consistently pushed for the production of electric vehicles that are both sustainable and affordable for the average consumer.
In a recent statement, Musk expressed a similar vision for Neuralink. He believes that, with advancements in manufacturing and widespread adoption, the cost of a Neuralink implant could eventually fall within the same price range as consumer electronics such as the Apple Watch, which costs around $300 to $500 for basic models. In fact, Musk has even suggested that in the near future, Neuralink devices could be priced as low as $1,000 to $2,000.
This is a bold claim, considering the complexity of the technology and the need for highly specialized surgical procedures to implant the device. Currently, the cost of developing and implanting a brain-computer interface is astronomically high, and the idea of making it affordable for the average person would require not only advancements in the technology itself but also dramatic reductions in production and surgical costs.
However, Musk’s confidence in achieving this goal is rooted in his past successes. For instance, the cost of electric cars has dramatically decreased over the years, thanks to economies of scale and advancements in manufacturing. Musk believes that Neuralink will follow a similar trajectory, where the cost of the technology will drop as the company scales and refines its processes.
The Path to Mass Adoption
In order for Neuralink to reach the affordability Musk envisions, several obstacles need to be overcome. First and foremost, the technology must become safe and effective for a wider range of people. While Neuralink has made significant strides in demonstrating the feasibility of its brain implant in animals, including a famous demonstration where a pig had a Neuralink device implanted to measure its brain activity, the technology still needs to undergo rigorous human trials before it can be considered safe for mainstream use.
Additionally, the surgical procedure to implant the device must be made less invasive and more cost-effective. Currently, the process is time-consuming and requires highly skilled neurosurgeons to ensure the implant is correctly positioned within the brain. Neuralink is working to automate this process with the development of a specialized robot that can perform the surgery with high precision. This robot, which is being tested as part of the company’s “600-second surgery” concept, could drastically reduce the time and cost associated with the procedure.
Moreover, public perception will play a crucial role in determining whether Neuralink can reach the masses. While many people are excited about the possibilities that BCIs offer, others are understandably concerned about the ethical implications and potential risks associated with implanting technology directly into the brain. Musk has acknowledged these concerns and emphasized that Neuralink is committed to ensuring the technology is used responsibly and transparently. Over time, as more people see the potential benefits, such as the ability to treat debilitating neurological conditions or enhance cognitive abilities, the public may become more open to the idea of brain implants.
Transforming Healthcare
One of the most exciting aspects of Neuralink’s work is its potential to revolutionize healthcare. The company is already focused on developing the technology to help people with neurological disorders. For individuals suffering from conditions such as paralysis or spinal cord injuries, a brain-computer interface could provide a life-changing opportunity. By bypassing damaged areas of the nervous system, a Neuralink implant could enable patients to control prosthetic limbs or interact with the world around them in ways they never thought possible.
In the future, Neuralink may also have applications in treating mental health conditions. For example, it could be used to regulate brain activity in patients with depression or anxiety, providing a non-invasive alternative to current treatments like medication or therapy. This could significantly improve the quality of life for millions of people around the world.
The Future of Human-Machine Interaction
While the immediate focus of Neuralink is on medical applications, Musk has hinted at broader uses for the technology in the future. He has spoken about the potential for enhancing human intelligence by connecting the brain directly to artificial intelligence (AI). In this scenario, humans would be able to interface with computers and AI systems without the need for external devices like keyboards, mice, or touchscreens.
Such advancements could lead to a new era of human-machine collaboration, where people can perform tasks at a speed and accuracy previously unimaginable. If Neuralink can achieve its goal of affordability and widespread adoption, it could mark the beginning of a new chapter in human evolution, one where the boundaries between biological and artificial intelligence are blurred.
Conclusion
Elon Musk’s dream of making Neuralink’s brain-computer interface as affordable as an Apple Watch is ambitious, but it is not beyond the realm of possibility. With continued innovation, advancements in manufacturing, and the development of more efficient surgical techniques, the technology could eventually become accessible to the masses. Whether Neuralink will be able to live up to its promises remains to be seen, but one thing is clear: if successful, it could revolutionize the way we interact with technology, offering new possibilities for both healthcare and human enhancement.
Related posts:
 Chilling Never-Before-Seen Footage of Twin Towers Collapse Surfaces After 23 Years
Chilling Never-Before-Seen Footage of Twin Towers Collapse Surfaces After 23 Years
 Following his Instagram revelation of cybertruck charging costs, David Nguyen ignites a debate.
Following his Instagram revelation of cybertruck charging costs, David Nguyen ignites a debate.
 Regarding parenthood, Neil Patrick Harris explains why he doesn’t know which twin is biologically his.
Regarding parenthood, Neil Patrick Harris explains why he doesn’t know which twin is biologically his.
 The Cause of Death of Paul Danan Is Verified
The Cause of Death of Paul Danan Is Verified
 Video of Obama “Announcing DOGE” 14 Years Before Acting with Trump Is Shared by Elon Musk
Video of Obama “Announcing DOGE” 14 Years Before Acting with Trump Is Shared by Elon Musk
 The Psychology and Science of Women’s Attraction to Older Men
The Psychology and Science of Women’s Attraction to Older Men
 Woman Fired After Boss Used Keystroke Technology To Monitor Her Working From Home
Woman Fired After Boss Used Keystroke Technology To Monitor Her Working From Home
 Genius Reason Why So Many Celebrities Wear Red Glasses
Genius Reason Why So Many Celebrities Wear Red Glasses